Chapter 3 - PATROLLING
Patrols are missions to gather information or to conduct combat
operations. Infantry platoons and squads conduct three types of
patrols: reconnaissance, combat and tracking, This chapter describer
the planning considerations used in preparation for patrols, conduct
of patrols, and establishment of and actions taken in a patrol base.
Section I. PLANNING CONSIDERATIONS
This section provides the planning considerations common to most patrols, the required tasks that guide the platoon and squad leader in organizing patrols, the initial planning and coordination requirements, and the coordination requirements for the departure and reentry of friendly lines.
3-1. ORGANIZATION
To accomplish the patrolling mission, a platoon or squad must perform specific tasks; for example, secure itself, danger area crossings, or rally points; reconnoiter the patrol objective; breach, support, or assault. As with other missions, the leader tasks elements of his platoon in accordance with his estimate of the situation. He identifies those tasks the platoon must perform and decides which elements will perform them. Where possible, in assigning tasks, the leader should maintain squad and fire team integrity. The chain of command continues to lead its elements during a patrol. The terms “element” and “team” refer to the squads, fire teams, or buddy teams that perform the tasks as described. Squads and fire teams may perform more than one task in an assigned Sequence others may perform only one task. The leader must plan carefully to ensure that he has identified and assigned all required tasks in the most efficient way. Elements and teams for platoons conducing patrols include the common and specific elements for each type of patrol. The following elements are common to all patrols.
a. Headquarters Element. The headquarters consists of the platoon leader, RATELO, platoon sergeant, FO, and FO RATELO. It may consist of any attachments that the platoon leader decides that he or the platoon sergeant must control directly.
b. Aid and Litter Team. Aid and litter teams are responsible for treating and evacuating casualties.
c. Enemy Prisoner of War Team. EPW teams are responsible for controlling enemy prisoners IAW the five S’s and the leader’s guidance.
d. Surveillance Team. The surveillance team keeps watch on the objective from the time that the leader’s reconnaissance ends until the unit deploys for actions on the objective. They then join their element.
e. En Route Recorder. The en route recorder records all information collected during the mission.
f. Compass Man. The compass man assists in navigation by ensuring the lead fire team leader remains on course at all times. Instructions to the compass man must include an initial azimuth with subsequent azimuths provided as necessary. The compass man should preset his compass on the initial azimuth before moving out, especially if the move will be during limited visibility conditions. The platoon or squad leader should also designate an alternate compass man.
g. Pace Man. The pace man maintains an accurate pace at all times. The platoon or squad leader should designate how often the pace man is to report the pace to him. The pace man should also report the puce at the end of each leg. The leader should also designate an alternate pace man.
3-2. INITIAL PLANNING AND COORDINATION
Leaders plan and prepare for patrols using the troop-leading procedure and the estimate of the situation. Leaders identify required actions on the objective, then plan backward to the departure from friendly lines and forward to the reentry of friendly lines. They normally receive the OPORD in the battalion or company CP where communications are good and key personnel are available. Because patrols act independently, move beyond the direct-fire support of the parent unit, and operate forward of friendly units, coordination must be thorough and detailed. Leaders normally coordinate directly with the battalion staff. They coordinate continuously throughout the planning and preparation phases. They use checklists to preclude omitting any items vital to the accomplishment of the mission.
a. Items coordinated between the leader and the battalion staff or company commander include–
-
Changes or updates in the enemy situation.
-
Best use of terrain for routes, rally points, and patrol bases.
-
Light and weather data.
-
Changes in the friendly situation.
-
The attachment of soldiers with special skills or equipment; for example, engineers, sniper teams, scout dog teams, FOs, or interpreters.
-
Use and location of landing zones.
-
Departure and reentry of friendly lines.
-
Fire support on the objective and along the planned routes, including alternate routes.
-
Rehearsal areas and times. The terrain for the rehearsal should be similar to that at the objective, to include buildings and fortifications if necessary. Coordination for rehearsals includes security of the area, use of blanks, pyrotechnics, and live ammunition.
-
Special equipment requirements.
-
Transportation support, including transportation to and from the rehearsal site.
-
Signal plan–call signs frequencies, code words, pyrotechnics, and challenge and password.
b. The leader coordinates with the unit through which his platoon or squad will conduct its forward and rearward passage of lines. (See paragraph 3-4 for specific items for coordination.)
c. The platoon leader also coordinates patrol activities with the leaders of other units that will be patrolling in adjacent areas at the same time.
3-3. COMPLETION OF THE PLAN
As the platoon leader completes his plan, he considers the following.
a. Essential and Supporting Tasks. The leader ensures that he has assigned all essential tasks to be performed on the objective, at rally points, at danger areas, at security or surveillance locations, along the route(s), and at passage lanes.
b. Key Travel and Execution Times. The leader estimates time requirements for movement to the objective, leader’s reconnaissance of the objective, establishment of security and surveillance, compaction of all assigned tasks on the objective, movement to an objective rally point to debrief the platoon, and return to and through friendly lines.
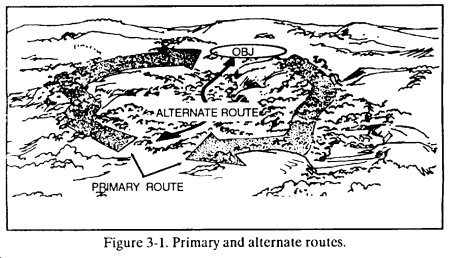
c. Primary and Alternate Routes. The leader selects primary and alternate routes to and from the objective (Figure 3-1). The return routes should differ from the routes to the objective.
d. Signals. The leader should consider the use of special signals. These include arm-and-hand signals, flares, voice, whistles, radios, and infrared equipment. All signals must be rehearsed so that all soldiers know what they mean.
e. Challenge and Password Forward of Friendly Lines. The challenge and password from the SOI must not be used beyond the FEBA.
(1) The platoon can use the odd-number system. The leader specifies an odd number. The challenge can be any number less than the specified number. The password will be the number that must be added to it to equal the specified number.
(2) The platoon leader can also designate a running password. This code word alerts a unit that friendly soldiers are approaching in a less than organized manner and possibly under pressure. This may be used to get soldiers quickly through a compromised passage of friendly lines. The running password is followed by the number of soldiers approaching (“Moosebreath five”). This prevents the enemy from joining a group in an attempt to penetrate a friendly unit.
f. Location of Leaders. The leader considers where he and the platoon sergeant and other key leaders should be located for each phase of the patrol mission. The platoon sergeant is normally with the following elements for each type of patrol:
-
On a raid or ambush, he normally controls the support element.
-
On an area reconnaissance, he normally stays in the ORP.
-
On a zone reconnaissance, he normally moves with the reconnaissance element that sets up the link-up point.
g. Actions on Enemy Contact. Unless required by the mission, the platoon avoids enemy contact. The leader’s plan must address actions on chance contact at each phase of the patrol mission. The platoon’s ability to continue the mission will depend on how early contact is made, whether the platoon is able to break contact successfully (so that its subsequent direction of movement is undetected), and whether the platoon receives any casualties as a result of the contact.
(1) The plan must address the handling of seriously wounded soldiers and KIAs.
(2) The plan must address the handling of prisoners who are captured as a result of chance contact and are not part of the planned mission.
h. Contingency Plans. The leader leaves for many reasons throughout the planning, coordination, preparation, and execution of his patrol mission. Each time the leader departs without radio or wire communications, he must issue a five-point contingency plan. The contingency plan includes–
-
Where the leader is going.
-
Who he is taking with him.
-
The amount of time he plans to be gone.
-
The actions taken if the leader dots not return.
-
The unit’s and the leader’s actions on chance contact while the leader is gone.
3-4. DEPARTURE FROM FRIENDLY LINES
The departure from friendly lines must be thoroughly planned and coordinated.
a. Coordination. The platoon leader must coordinate with the commander of the forward unit and the leaders of other units that will be patrolling in the same or adjacent areas. The coordination includes SOI information, signal plan, fire plan, running password, procedures for departure and reentry lines, dismount points, initial rally points, departure and reentry points, and information about the enemy.
(1) The platoon leader provides the forward unit leader with the unit identification, the size of the patrol, the departure and return times, and the area of operation.
(2) The forward unit leader provides the platoon leader with the following:
-
Additional information on terrain.
-
Known or suspected enemy positions.
-
Likely enemy ambush sites.
-
Latest enemy activity.
-
Detailed information on friendly positions and obstacle locations. This includes the location of OPs.
-
Friendly unit fire plan.
-
Support that the unit can provide; for example, fire support, litter teams, guides, communications, and reaction force.
b. Planning. In his plan for the depature of friendly lines, the leader should consider the following sequence of actions:
-
Making contact with friendly guides at the contact point.
-
Moving to the coordinated initial rally point.
-
Completing final coordination.
-
Moving to and through the passage point.*
-
Establishing a security-listening halt beyond the friendly unit’s final protective fires.
3-5. RALLY POINTS
The leader considers the use and locations of rally points. A rally point is a place designated by the leader where the platoon moves to reassemble and reorganize if it becomes dispersed.
a. Selection of Rally Points. The leader physically reconnoiters routes to select rally points whenever possible. He selects tentative points if he can only conduct a map reconnaissance. He confirms them by actual inspection as the platoon moves through them. Rally points must–
-
Be easy to find.
-
Have cover and concealment.
-
Be away from natural lines of drift.
-
Be defendable for short periods.
b. Types of Rally Points. The most common types of rally points are initial, en route, objective, reentry, and near- and far-side rally points. Soldiers must know which rally point to move to at each phase of the patrol mission. They should know what actions are required there and how long they are to wait at each rally point before moving to another.
(1) Initial rally point. An initial rally point is a place inside of friendly lines where a unit may assemble and reorganize if it makes enemy contact during the departure of friendly lines or before reaching the first en route rally point. It is normally selected by the commander of the friendly unit.
(2) En route rally point. The leader designates en route rally points every 100 to 400 meters (based on the terrain, vegetation, and visibility). When the leader designates a new en route rally point, the previously designated one goes into effect. This precludes uncertainty over which one soldiers should move to if contact is made immediately after the leader designates a new rally point. There are three ways to designate a rally point:
(a) Physically occupy them for a short period. This is the preferred method.
(b) Pass by at a distance and designate using arm-and-hand signals.
(c) Walk through and designate using arm-and-hand signals.
(3) Objective rally point. The objective rally point (ORP) is a point out of sight, sound, and small-arms range of the objective area. It is normally located in the direction that the platoon plans to move after completing its actions on the objective. The ORP is tentative until the objective is pinpointed. (Figure 3-2.) Actions at or from the ORP include–
-
Reconnoitering the objective.
-
Issuing a FRAGO.
-
Disseminating information from reconnaissance if contact was not made.
-
Making final preparations before continuing operations; for example, recamouflaging: preparing demolitions; lining up rucksacks for quick recovery; preparing EPW bindings, first aid kits, and litters; and inspecting weapons.
-
Accounting for soldiers and equipment after actions at the objective are complete.
-
Reestablishing the chain of command after actions at the objective are complete.
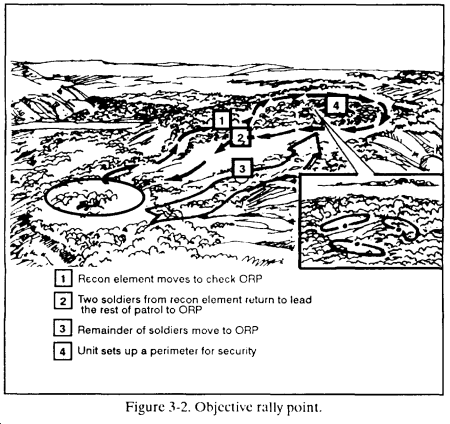
(a) Occupation of an ORP by a squad. In planning the occupation of an ORP, the squad leader considers the following sequence:
-
Halt beyond sight, sound, and small-arms weapons range of the tentative ORP (200 to 400 meters in good visibility; 100 to 200 meters in limited visibility).
-
Position security.
-
Move forward with a compass man and one member of each fire team to confirm the location of the ORP and determine its suitability. Issue a five-point contingency plan before departure.
-
Position the Team A soldier at 12 o’clock, and the Team B soldier at 6 o’clock in the ORF. Issue them a contingency plan and return with the compass man.
-
Lead the squad into the ORP, position Team A from 9 to 3 o’clock and Team B from 3 to 9 o’clock.
NOTE: The squad may also occupy the ORP by force. This requires more precise navigation, but eliminates separating the squad.
(c) Occupation of an ORP by a platoon. The platoon leader should consider the same sequence in planning the occupation of an ORP. He brings a soldier from each squad on his reconnaissance of the ORP and positions them at the 10, 2, and 6 o’clock positions. The first squad in the order of march establishes the base leg (10 to 2 o’clock). The trailing squads occupy from 2 to 6 o’clock and 6 to 10 o’clock, respectively.
(4) Reentry rally point. The reentry rally point is located out of sight, sound, and small-arms weapons range of the friendly unit through which the platoon will return. This also means that the RRP should be outside the final protective fires of the friendly unit. The platoon occupies the RRP as a security perimeter.
(5) Near-and far-side rally points. These rally points are on the near and far side of danger areas. If the platoon makes contact while crossing the danger area and control is lost, soldiers on either side move to the rally point nearest them. They establish security, reestablish the chain of command, determine their personnel and equipment status, and continue the patrol mission, link up at the ORP, or complete their last instructions.
3-6. LEADER’S RECONNAISSANCE OF THE OBJECTIVE
The plan must include a leader’s reconnaissance of the objective once t he platoon or squad establishes the ORF. During his reconnaissance, the leader pinpoints the objective; selects security, support, and assault positions for his squads and fire teams; and adjusts his plan based on his observation of the objective. Each type of patrol requires different tasks during the leader’s reconnaissance. The platoon leader will take different elements with him. The leader must plan time to return to the ORP, complete his plan, disseminate information, issue orders and instructions, and allow his squads to make any additional preparations.
3-7. REENTRY OF FRIENDLY LINES
The platoon leader’s initial planning and coordination must include the reentry of friendly lines. The platoon leader should consider the following sequence.
WARNING____________________________________________________________
Reentry of friendly lines at night is dangerous and should only be attempted when it is essential to the success of the patrol.
a. The platoon halts in the RRP and establishes security.
b. The platoon leader radios the code word advising the friendly unit of its location and that it is ready to return. The friendly unit must acknowledge the message and confirm that guides are waiting before the platoon moves from the RRP.
(1) If radio communications are not possible, the platoon leader, RATELO, and a two-man (buddy team) security element move forward and attempt to contact an OP using the challenge and password. The OP notifies the friendly unit that the platoon is ready to return and requests a guide.
(2) If the platoon leader cannot find an OP, he moves with the RATELO and security element to locate the coordinated reentry point. He must move straight toward (and away from) friendly lines, never parallel to them. All lateral movement should be outside of small-arms weapons range.
NOTE: The platoon leader should only attempt this procedure during daylight. At night he should use other backup signals to make contact with friendly units. The preferred method is to wait until daylight if contact with the friendly unit cannot be made as planned.
c. Once the friendly unit acknowledges the return of the platoon, the platoon leader issues a five-point contingency plan and moves with his RATELO and a two-man (buddy team) security element on a determined azimuth and pace to the reentry point.
d. The platoon leader uses far and near recognition signals to establish contact with the guide.
e. The platoon leader signals the platoon forward (radio) or returns and leads it to the reentry point. He may post the security element with the guide at the enemy side of the reentry point.
f. The platoon sergeant counts and identifies each soldier as he passes through the reentry point.
g. The guide leads the platoon to the assembly area.
h. The platoon leader reports to the command post of the friendly unit. He tells the commander everything of tactical value concerning the friendly unit’s area of responsibility.
i. The platoon leader rejoins the platoon in the assembly area and leads it to a secure area for debriefing.
3-8. DEBRIEFING
Immediately after the platoon or squad returns, personnel from higher headquarters conduct a thorough debrief. This may include all members of the platoon or the leaders, RATELOs, and any attached personnel. Normally the debriefing is oral. Sometimes a written report is required. NATO forces use the patrol report form specified by STANAG 2003. Information on the written report should include–
-
Size and composition of the platoon conducting the patrol.
-
Mission of the platoon (type of patrol, location, purpose).
-
Departure and return times.
-
Routes. Use check points, grid coordinates for each leg or include an overlay.
-
Detailed description of terrain and enemy positions that were identified.
-
Results of any contact with the enemy.
-
Personnel status at the conclusion of the patrol mission, including the disposition of casualties.
-
Conclusions or recommendations.
Section II. RECONNAISSANCE PATROL
The three types of reconnaissance patrols are area, zone, and route. Reconnaissance patrols provide timely and accurate information on the enemy and terrain. They confirm the leader’s plan before it is executed. The commander must inform the leader of the specific information requirements for each mission.
3-9. ORGANIZATION
Besides the common elements, reconnaissance patrols have a reconnaissance team and a reconnaissance and security team.
a. Reconnaissance Team. Reconnaissance teams reconnoiter the objective area once the security teams are in position. Normally these are two-man teams (buddy teams) to reduce the possibility of detection.
b. Reconnaissance and Security Team. R&S teams are normally used in a zone reconnaissance, but may be useful in any situation when it is impractical to separate the responsibilities for reconnaissance and security.
3-10. TASKS TO SUBORDINATE UNITS
Normally the platoon headquarters element controls the platoon on a reconnaissance patrol mission.
a. The platoon leader must consider the requirements for reconnaissance and security in assigning tasks to his squads or fire teams. He may separate the tasks so that one or more squads conduct the reconnaissance while other squads or fire teams provide security at various locations. Or, he may assign reconnaissance and security (R&S) tasks to each squad or team. When a fire team conducts a reconnaissance patrol it operates as a single R&S team.
b. In assigning tasks, the leader must also consider the size and number of reconnaissance objectives, the requirement to secure the ORP and other points, and the time allowed for conducting the mission.
3-11. AREA RECONNAISSANCE
An area reconnaissance is conducted to obtain information about a specified location and the area around it. The location may be given as a grid coordinate or an objective on an overlay. In an area reconnaissance, the platoon or squad uses surveillance or vantage-points around the objective from which to observe it and the surrounding area. In planning for an area reconnaissance mission, the platoon leader considers the following sequence of actions.
a. The leader may include a surveillance team in his reconnaissance of the objective from the ORP. He positions it while on the reconnaissance. The subordinate leader responsible for security establishes security at the ORP and positions other security teams as required on likely enemy avenues of approach into the objective area.
b. If required the leader positions other surveillance elements about the objective. He may move them on one route, posting them as they move, or he may direct them to move on separate routes to their assigned locations.
c. After observing the objective for a specified time, all elements return to the ORP and report their observations to the leader or the recorder. Once all information is collected, it is disseminated to every soldier.
3-12. ZONE RECONNAISSANCE
A zone reconnaissance is conducted to obtain information on enemy, terrain, and routes within a specified zone. Zone reconnaissance techniques include the use of moving elements, stationary teams, or a series of area reconnaissance actions.
a. Moving Elements. The leader plans the use of squads or fire teams moving along multiple routes to cover the entire zone. Methods for planning the movement of multiple elements through a zone include the fan, the box, converging routes, and successive sectors.
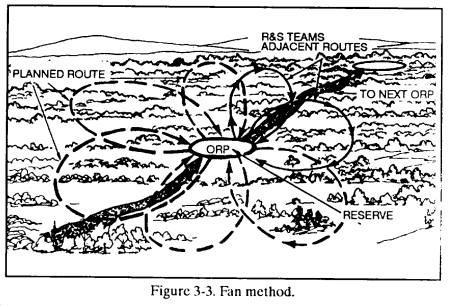
(1) Fan method. The leader first selects a series of ORPs throughout the zone. The platoon establishes security at the first ORP. Each R&S team moves from the ORP along a different fan-shaped route that overlaps with others to ensure reconnaissance of the entire area. The leader maintains a reserve at the ORP. When all R&S teams have returned to the ORP, the platoon collects and disseminates all information to every soldier before moving on to the next ORP. (Figure 3-3.)
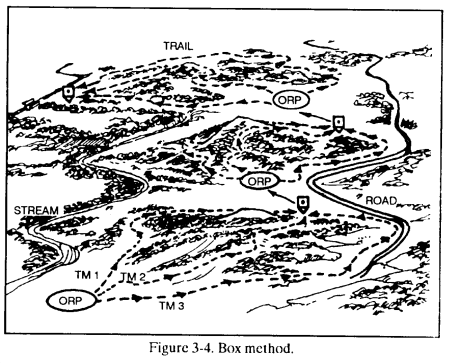
(2) Box method. The leader sends his R&S teams from the ORP along routes that form a boxed-in area. He sends other teams along routes through the area within the box. All teams meet at a link-up point at the far side of the box from the ORP. (Figure 3-4.)
(3) Converging routes method. The leader selects routes from the ORP through the zone to a link-up point at the far side of the zone from the ORP. Each R&S team moves along a specified route and uses the fan method to reconnoiter the area between routes. The leader designates a time for all teams to link-up. (Figure 3-5.)
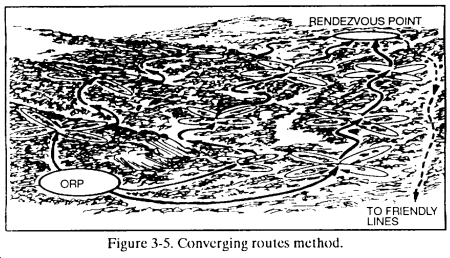
(4) Successive sector method. The leader may divide the zone into a series of sectors. Within each sector, the platoon uses the converging routes method to reconnoiter to an intermediate link-up point where it collects and disseminates the information gathered to that point before reconnoitering the next sector. (Figure 3-6.)
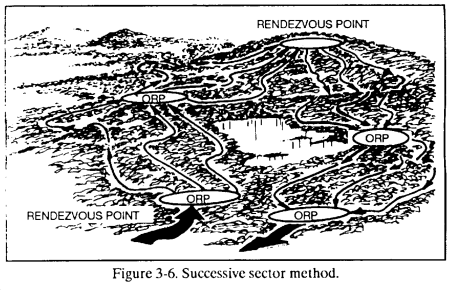
b. Stationary Teams. Using this technique, the leader positions surveillance teams in locations where they can collectively observe the entire zone for long-term, continuous information gathering (Figure 3-7). He must consider sustainment requirements when developing his soldier’s load plan.

c. Multiple Area Reconnaissance. The leader tasks each of his squads to conduct a series of area reconnaissance actions along a specified route. (Figure 3-8.)

3-13. ROUTE RECONNAISSANCE
A route reconnaissance is conducted to obtain detailed information about one route and all the adjacent terrain or to locate sites for emplacing obstacles. A route reconnaissance is oriented on a road; a narrow axis, such as an infiltration lane; or a general direction of attack. Normally engineers are attached to the infantry unit for a complete route reconnaissance. Infantry can conduct a hasty route reconnaissance without engineer support. A route reconnaissance results in detailed information about trafficability, enemy activity, NBC contamination, and aspects of adjacent terrain from both the enemy and friendly viewpoint. In planning a route reconnaissance the leader considers the following.
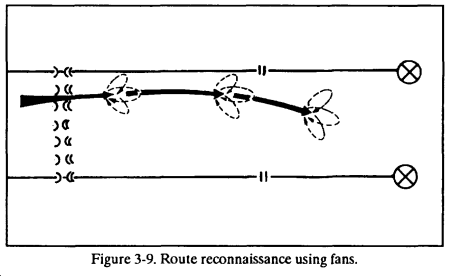
a. The preferred method for conducting a route reconnaissance is the fan method described above. The leader must ensure that the fans are extensive enough to reconnoiter intersecting routes beyond direct-fire range of the main route. (Figure 3-9.)
b. The platoon should use a different return route.
c. If all or part of the proposed route is a road, the leader must treat the road as a danger area. The platoon moves parallel to the road using a covered and concealed route. When required, reconnaissance and security teams move close to the road to reconnoiter key areas.
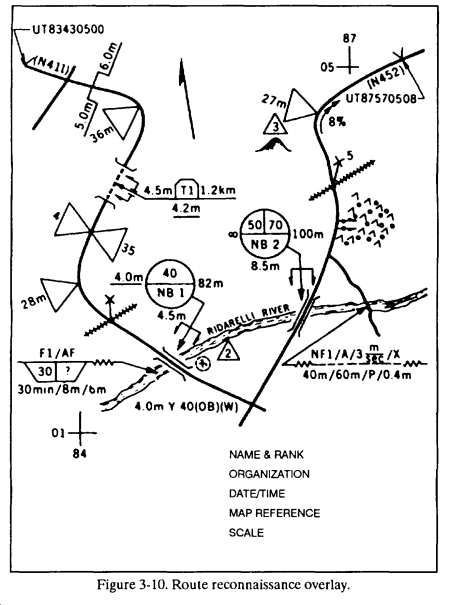
d. The leader should submit the patrol report in an overlay format LAW FM 5-34 or GTA 5-2-5 ( Figure 3-10).
Section III. COMBAT PATROL
Combat patrols are conducted to destroy or capture enemy soldiers or equipment; destroy installations, facilities, or key points; or harass enemy forces. They also provide security for larger units. The two types of combat patrol missions are ambush and raid.
3-14. ORGANIZATION
Besides the common elements, combat patrols also have the following elements and teams.
a. Assault Element. The assault element seizes and secures the objective and protects special teams as they complete their assigned actions on the objective.
b. Security Element. The security element provides security at danger areas, secures the ORP, isolates the objective, and supports the withdrawal of the rest of the platoon once it completes its assigned actions on the objective. The security element may have separate security teams, each with an assigned task or sequence of tasks.
c. Support Element. The support element provides direct fire support and may control indirect fires for the platoon.
d. Breach Element. The breach element breaches the enemy’s obstacles when required.
e. Demolition Team. Demolition teams are responsible for preparing and exploding the charges to destroy equipment, vehicles, or facilities on the objective.
f. Search Team. The assault element may comprise two-man (buddy teams) or four-man (fire team) search teams to search bunkers, buildings, or tunnels on the objective. These teams may search the objective or kill zone for casualties, documents, or equipment.
3-15. TASKS TO SUBORDINATE UNITS
Normally the platoon headquarters element controls the platoon on a combat patrol mission. The platoon leader must make every attempt to maintain squad and fire team integrity as he assigns tasks to subordinate units.
a. The platoon leader must consider the requirements for assaulting the objective, supporting the assault by fire, and securing the platoon throughout the mission.
(1) For the assault on the objective, the leader must consider the required actions on the objective, the size of the objective, and the known or presumed strength and disposition of the enemy on and near the objective.
(2) The leader must consider the weapons available, and the type and volume of fires required to provide fire support for the assault on the objective.
(3) The leader must consider the requirement to secure the platoon at points along the route, at danger areas, at the ORP, along enemy avenues of approach into the objective, and elsewhere during the mission.
b. The leader must assign additional tasks to his squads for demolition, search of enemy killed and captured, guarding of EPWs, treatment and evacuation (litter teams) of friendly casualties, and other tasks required for successful completion of the patrol mission.
c. The platoon leader must determine who will control any attachments of skilled personnel or special equipment.
3-16. LEADER’S RECONNAISSANCE OF THE OBJECTIVE
In a combat patrol, the leader has additional considerations for the conduct of his reconnaissance of the objective from the ORP. He is normally the assault element leader. He should also take the support element leader, the security element leader, and a surveillance team (a two-man team from the assault element).
a. The leader should designate a release point halfway between the ORP and the objective. Squads and fire teams separate at the release point and move to their assigned positions. The release point should have wire communications with the ORP and be set up so that other elements can tie into a hot loop there.
b. The platoon leader should confirm the location the objective and determine that it is suitable for the assault or ambush. He notes the terrain and identifies where he can place mines or Claymores to cover dead space. He notes any other features of the objective that may cause him to alter his plan.
c. If the objective is the kill zone for an ambush, the leader’s reconnaissance party should not cross the objective, to do so will leave tracks that may compromise the mission.
d. The platoon leader should confirm the suitability of the assault and support positions and routes from them back to the ORP.
e. The platoon leader should post the surveillance team and issue a five-point contingency plan before returning to the ORP.
3-17. AMBUSH
An ambush is a surprise attack from a concealed position on a moving or temporarily halted target. Antiarmor ambushes are established when the mission is to destroy enemy armored or mechanized forces. Ambushes are classified by category--hasty or deliberate; type--point or area; and formation--linear or L-shaped. The leader uses a combination of category, type, and formation in developing his ambush plan.
a. Planning. The key planning considerations include–
-
Covering the entire kill zone by fire.
-
Using existing or reinforcing obstacles (Claymores and other mines) to keep the enemy in the kill zone.
-
Protecting the assault and support elements with mines, Claymores, or explosives.
-
Using security elements or teams to isolate the kill zone.
-
Assaulting into the kill zone to search dead and wounded, assemble prisoners, and collect equipment. (The assault element must be able to move quickly through its own protective obstacles.)
-
Timing the actions of all elements of the platoon to preclude loss of surprise.
-
Using only one squad to conduct the entire ambush and rotating squads over time from the ORP. This technique is useful when the ambush must be manned for a long time.
b. Formations. The leader considers the linear or L-shaped formations in planning an ambush.
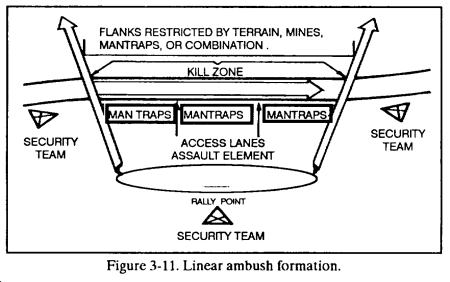
(1) Linear. In an ambush using a linear formation, the assault and support elements deploy parallel to the enemy’s route (Figure 3-11). This positions both elements on the long axis of the kill zone and subjects the enemy to flanking fire. This formation can be used in close terrain that restricts the enemy’s ability to maneuver against the platoon, or in open terrain provided a means of keeping the enemy in the kill zone can be effected.
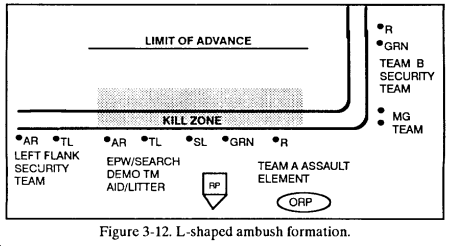
(2) L-shaped. In an L-shaped ambush, the assault element forms the long leg parallel to the enemy’s direction of movement along the kill zone. The support element forms the short leg at one end of and at right angles to the assault element. This provides both flanking (long leg) and enfilading fires (short leg) against the enemy. The L-shaped ambush can be used at a sharp bend in a trail, road, or stream. It should not be used where the short leg would have to cross a straight road or trail. (Figure 3-12.)
3-18. HASTY AMBUSH
A platoon or squad conducts a hasty ambush when it makes visual contact with an enemy force and has time to establish an ambush without being detected. The actions for a hasty ambush must be well rehearsed so that soldiers know what to do on the leader’s signal. They must also know what action to take if detected before they are ready to initiate the ambush. The conduct of a hasty ambush is discussed below. In planning and rehearsing a hasty ambush the platoon leader should consider the following sequence of actions:
a. Using visual signals, any soldier alerts the platoon that an enemy force is in sight. The soldier continues to monitor the location and activities of the enemy force until he is relieved by his team or squad leader.
b. The platoon or squad halts and remains motionless.
c. The leader determines the best nearby location for a hasty ambush. He uses arm-and-hand signals to direct soldiers to covered and concealed positions. The leader designates the location and extent of the kill zone.
d. Security elements move out to cover each flank and the rear. The leader directs the security elements to move a given distance, set up, and rejoin the platoon on order or, after the ambush (the sound of firing ceases). At squad level, the two outside buddy teams normally provide flank security as well as fires into the kill zone (Figure 3-13). At platoon level, fire teams make up the security elements (Figure 3-14).
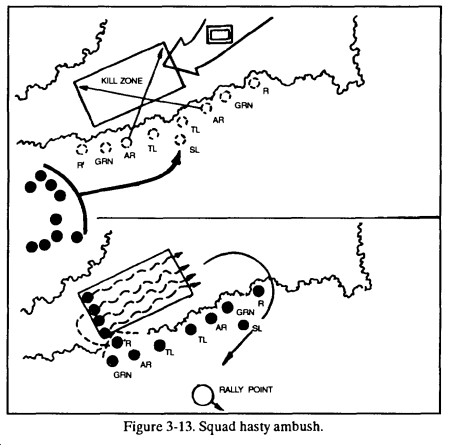
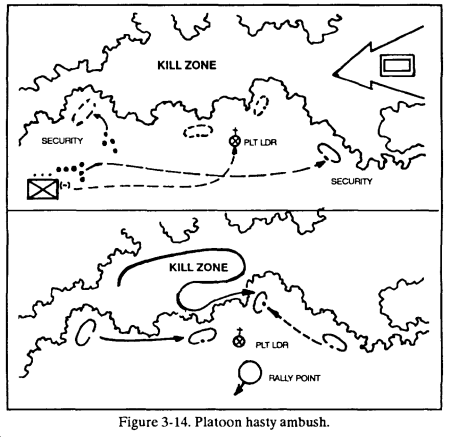
e. Soldiers move quickly to covered and concealed positions, normally 5 to 10 meters apart. Soldiers ensure that they have good observation and fields of fire into the kill zone.
f. The leader initiates the ambush when the majority of the enemy force enters the kill zone. (If time and terrain permit, the squad or platoon may place out Claymores and use them to initiate the ambush.)
NOTE: If the enemy detects a soldier, the soldier initiates the ambush by firing his weapon and alerting the rest of the platoon, saying ENEMY RIGHT (LEFT or FRONT).
g. Leaders control the rate and distribution of fires. The leader orders cease fire when the enemy force is destroyed or ceases to resist. Directs the assault element to move into the kill zone and conduct a hasty search of the enemy soldiers. All other soldiers remain in place to provide security.
h. The security elements rejoin the platoon after the assault element has cleared through the kill zone. The platoon withdraws from the ambush site using a covered and concealed route. The platoon returns to the ORP in effect, collects and disseminates all information, reorganizes as necessary and continues the mission.
3-19. DELIBERATE AMBUSH
A deliberate ambush is conducted against a specific target at a predetermined location. The leader requires detailed information in planning a deliberate ambush:
-
Size and composition of the targeted enemy unit.
-
Weapons and equipment available to the enemy.
-
The enemy’s route and direction of movement.
-
Times that the targeted unit will reach or pass specified points along the route.
3-20. POINT AMBUSH
In a point ambush, soldiers deploy to attack an enemy in a single kill zone. The platoon leader should consider the following sequence of actions when planning a deliberate point ambush:
a. The security or surveillance team(s) should be positioned first. The support element should be in position before the assault element moves forward of the release point. The support element must overwatch the movement of the assault element into position.
b. The platoon leader is the leader of the assault element. He must check each soldier once they establish the assault position. He signals the surveillance team to rejoin the assault element.
(1) Actions of the assault element should include–
-
Identify individual sectors of fire as assigned by the platoon leader. Emplace aiming stakes.
-
Emplace Claymores and other protective devices.
-
Emplace Claymores, mines, or other explosives in dead space within the kill zone.
-
Camouflage positions.
-
Take weapons off SAFE. Moving the selection lever on the weapon causes a metallic click that could compromise the ambush if soldiers wait until the enemy is in the kill zone. This must be the last action performed by all soldiers before waiting to initiate the ambush.
(2) Actions of the support element include–
-
Identify sectors of fire for all weapons, especially machine guns. Emplace limiting stakes to prevent friendly fires from hitting the assault element in an L-shaped ambush.
-
Emplace Claymores and other protective devices.
c. Instructions to security teams must include how to notify the platoon leader of the enemy’s approach into the kill zone (SALUTE report). The security element must also keep the platoon leader in formed if any enemy forces are following the lead force.
d. The platoon leader must determine how large an element his ambush can engage successfully. He must be prepared to let units pass that are too large. He must report to higher headquarters any units that pass his ambush unengaged.
e. The platoon leader initiates the ambush. He may use a command detonated Claymore. He must also plan a backup method for initiating the ambush should the primary means fail. This should also be a casualty-producing device such as a machine gun. This information must be passed out to all soldiers and practiced during rehearsals.
f. Soldiers must have a means of engaging the enemy in the kill zone during periods of limited visibility if it becomes necessary to initiate the ambush then. Use of tracers must be weighed against how it might help the enemy to identify friendly positions. The platoon leader may use handheld or indirect illumination flares.
g. The platoon leader should include indirect fire support as a part of his plan. Indirect fires can cover the flanks of the kill zone to help isolate it. They can also help the platoon to disengage if the ambush is compromised or the platoon must depart the ambush site under pressure.
h. The platoon leader must have a good plan to signal the advance of the assault element into the kill zone to begin its search and collection activities. Smoke may not be visible to the support element. All soldiers must know and practice relaying this signal during rehearsals.
i. The assault element must be prepared to move across the kill zone using individual movement techniques if there is any return fire once they begin to search. Otherwise the assault element moves across by bounding fire teams. Other actions in the kill zone include the following.
(1) Collect and secure all EPWs and move them out of the kill zone before searching bodies. Establish a location for EPWs and enemy wounded who will not be taken back that provides them cover, yet allows them to be found easily by their units.
(2) Search from one side to the other and mark bodies that have been searched to ensure the area is thoroughly covered.
(3) Use the two-man search technique.
(a) As the search team approaches a dead enemy soldier, one man guards while the other man searches. First, he kicks the enemy weapon away. Second, he rolls the body over (if on the stomach) by laying on top and when given the go ahead by the guard (who is positioned at the enemy’s head), the searcher rolls the body over on him. This done for protection in case the enemy soldier has a grenade with the pin pulled underneath him.
(b) The searchers then conduct a systematic search of the dead soldier from head to toe removing all papers and anything new (different type rank, shoulder boards, different unit patch, pistol, weapon, or NVD). They note if the enemy has a fresh or shabby haircut and the condition of his uniform and boots. They take note of the radio frequency, SOI, and maps. Once the body has been thoroughly searched, the search team will continue in this manner until all enemy personnel in and near the kill zone have been searched. Enemy bodies should be marked (for example, fold arms over chest) to avoid duplication.
(4) Identify and collect equipment to be carried back. Prepare it for transport. (Clear all weapons and place them on SAFE.)
(5) Identify and collect remaining equipment for destruction. The demolition team prepares dual-primed explosives (C4 with two M60 fuse lighters and time fuse) and awaits the signal to initiate. This is normally the last action performed before departing the objective and may signal the security elements to return to the ORP.
(6) Treat friendly wounded first, then enemy wounded, time permitting.
j. The flank security teams may also place out antiarmor mines after the ambush has been initiated if the enemy is known to have armor capability. If a flank security team makes contact, it fights as long as possible without becoming decisively engaged. It uses a prearranged signal to let the platoon leader know it is breaking contact. The platoon leader may direct a portion of the support element to assist the security team in breaking contact.
k. The platoon leader must plan the withdrawal from the ambush site:
(1) Elements normally withdraw in the reverse order that they established their positions.
(2) The elements may return first to the release point, then to the ORP, depending on the distance between elements.
(3) The security element at the ORP must be alert to assist the platoon’s return to the ORP. It maintains security for the ORP while the rest of the platoon prepares to leave.
l. Actions back at the ORP include accountability of personnel and equipment and recovery of rucksacks and other equipment left at the ORP during the ambush.
3-21. AREA AMBUSH
In an area ambush, soldiers deploy in two or more related point ambushes. The platoon leader should consider the following sequence of actions when planning a deliberate area ambush.
a. A platoon is the smallest unit to conduct an area ambush. Platoons conduct area ambushes where enemy movement is largely restricted to trails or streams (Figure 3-15).
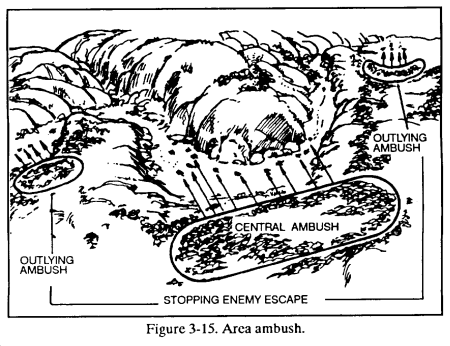
b. The platoon leader should select one principal ambush site around which he organizes outlying ambushes. These secondary sites are located along the enemy’s most likely approach to and escape from the principal ambush site. Squad-sized elements are normally responsible for each ambush site. They establish an area ambush as described above.
c. The platoon leader must determine the best employment of his machine guns. He normally positions them both with the support element of the principal site.
d. Squads responsible for outlying ambushes do not initiate their ambushes until after the principal one is initiated. They then engage to prevent enemy forces from escaping or reinforcing.
3-22. ANTIARMOR AMBUSH
Platoons and squads conduct antiarmor ambushes to destroy one or two armored vehicles. If a squad is given the mission to conduct an antiarmor ambush, it should have a MAW team attached to it. (Figure 3-16). The leader considers the following when planning an antiarmor ambush.
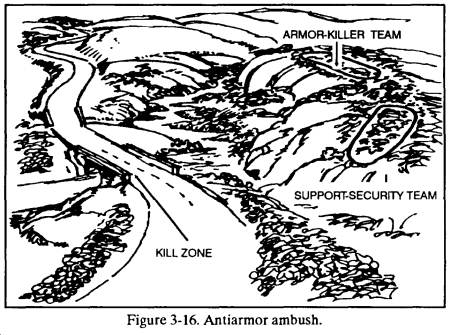
a. The armor-killer team is built around the MAW team. The leader must consider additional weapons available to supplement its fires. These are normally LAWs or AT4s. The leader must carefully position all antiarmor weapons to ensure the best shot (rear, flank, or top). The remainder of the platoon must function as support and security elements in the same way that they do for other combat patrols.
b. In a squad antiarmor ambush, the platoon leader selects the general site for the ambush. The squad leader must find a site that restricts the movement of armored vehicles out of the kill zone. The leader should attempt to place his elements so that an obstacle is between them and the kill zone.
c. Security elements must consider dismounted avenues of approach into the ambush site.
d. The leader should consider the method for initiating the antiarmor ambush. The preferred method is to use a command-detonated antiarmor mine placed in the kill zone. The MAW can be used to initiate the ambush, but its signature and slow rate of fire make it less desirable.
e. The armor-killer team attempts to kill the first and last vehicles in the column, if possible. All other weapons open fire once the ambush has begun. If the kill zone is within range of light antiarmor weapons, each soldier fires one during the ambush.
f. The leader must consider how the presence of dismounted enemy with the tanks will affect the success of his ambush. The leader’s choices include–
-
Initiate the ambush as planned.
-
Withdraw without initiating the ambush.
-
Initiate the ambush using only automatic weapons without firing antiarmor weapons.
g. Because of the speed with which other armored forces can reinforce the enemy in the ambush site, the leader should plan to keep the engagement short, and the withdrawal quick. The platoon will not clear through the kill zone as in other ambushes.
3-23. RAID
A raid is a combat operation to attack a position or installation followed by a planned withdrawal. Squads do not execute raids. The sequence of platoon actions for a raid is similar to those for an ambush. Additionally, the assault element of the platoon may have to conduct a breach of an obstacle. It may have additional tasks to perform on the objective; for example, demolition of freed facilities.
Section IV. TRACKING PATROL
A platoon or squad may receive the mission to follow the trail of a specific enemy unit. Soldiers looks for signs left by the enemy. They gather information about the enemy unit, the route, and the surrounding terrain as they track.
3-24. CONSIDERATIONS
The key considerations for conducting a tracking patrol include–
-
The soldiers move stealthily. The soldiers must be well-disciplined and well-trained in tracking techniques.
-
When the platoon receives the mission to conduct a tracking patrol, it assigns the task of tracking to only one squad. The remaining squads and attachments provide security.
-
The configuration of the platoon must provide security for the tracking team to the front and flanks as it follows the trail. The formation of a squad conducting a tracking patrol is in Figure 3-17. Separate elements of the squad must move as dispersed from each other as terrain and vegetation allows, and still maintain visual contact. Normally, the lead fire team is responsible for point security, tracking, and navigation.
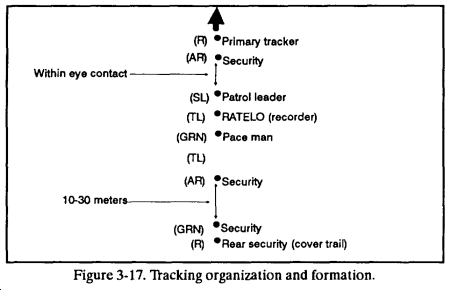
3-25. ORGANIZATION
Besides the common elements, tracking patrols have a security team and a tracking team.
a. Security Team. The security teams provide security for the squad leader, RATELO, and pace man and also provide rear and flank security.
b. Tracking Team. The tracking team reads signs and follows the track of a specific enemy unit.
3-26. TASKS TO SUBORDINATES
The most important consideration in assigning duties is the requirement to put the soldier best trained in tracking as the primary tracker. The squad leader attempts to maintain fire team and, if possible, buddy team integrity. He assigns the following duties to his soldiers.
a. Patrol Leader. The squad leader is the patrol leader and the main navigator. He has overall responsibility for mission accomplishment.
b. Primary Tracker. This soldier’s only task is to follow the main trail of the main body of the unit being tracked.
c. Security Man. This soldier provides security for the primary tracker. When possible, he is the primary tracker’s buddy team member.
c. Security Team. One buddy team provides security for the squad leader, the pace man, and RATELO.
d. Rear Security Team. One buddy team provides rear security for the squad.
3-27. TRAINING
Training is essential to develop and maintain the necessary tracking skills. Once deployed into an area of operation, training continues so the platoon can learn about local soil, climate, vegetation, animals, vehicles, footwear, and other factors. The primary tracker can prepare a tracking book showing specific signs and how they weather or change over time.
3-28. INTELLIGENCE
Specific intelligence about enemy habits, equipment, garment, footwear, diet, or tactics is important. For example, reports might show that the enemy wears sandals like the natives in the area. However, the units being tracked show signs of one soldier wearing boots with an unfamiliar tread. This could mean that the unit has a trained cadre, a foreign advisor, or a prisoner with it. Any specific information about the enemy is also helpful. If possible, soldiers should interview someone who has seen them.
3-29. TRAIL SIGNS
Men, machines, and animals leave signs of their presence as they move through an area. These signs can be as subtle as an odor, or as obvious as a well-worn path. All soldiers can read obvious signs such as roads, worn trails, or tracks in sand or snow. However, attention to detail, common sense, staying alert, logic, and knowledge of the environment and enemy habits allow soldiers to obtain better information from signs they find in the battle area.
a. Finding the Trail. Finding the trail is the first task of the tracking team. The tracking team can reconnoiter around a known location of enemy activity when the trail cannot be found in the immediate area. There are two ways they can hunt for the trail:
(1) From a known location. Often there is a specific area or location where the enemy has been seen. From here, the tracking team can locate and follow the enemy’s trail.
(2) Cutting trail. This occurs when the route of a friendly unit crosses a trail left by another group (Figure 3-18). It can be by chance or the team can deliberately choose a route that cuts across one or more probable enemy routes.
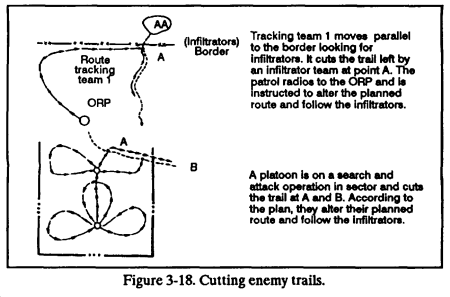
b. Trail and Sign Analysis. Once the first sign is discovered, it must not be disturbed or covered. It is analyzed carefully before following the enemy. If the sign is found at the site of enemy activity, the exact occurrence can often be reconstructed. If a trail is the first sign found, the tracker can still determine such facts as the size and composition of groups being tracked, their directions, their general condition, and other facts. The tracker determines as much as possible about the enemy before following them. As the platoon goes on, this process does also, and the tracker’s knowledge of the enemy grows. One or more of these techniques can be combined when the enemy attacks or tries to evade being tracked.
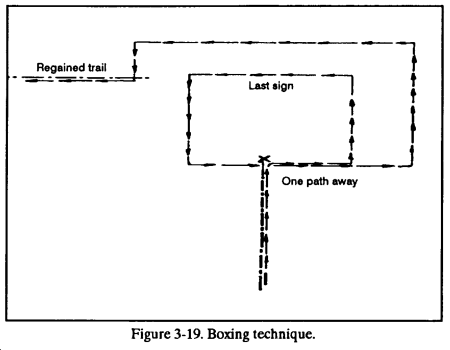
(1) Regaining a lost trail. As soon as the tracker loses the trail, he stops. The tracking team then retraces its path to the last enemy sign. It marks this point. The team studies the sign and the area around it for any clue as to where the enemy went. It looks for signs of the enemy scattering, backtracking, doglegging, or using any other countertracking method. If the trail is still lost, the team establishes security in a spot that avoids destroying any sign. The tracker and an assistant look for the trail. They do this by “boxing” the area around the last clear sign (Figure 3-19). The tracking team always returns to the same path, away from the last sign, to avoid creating more trails than needed.
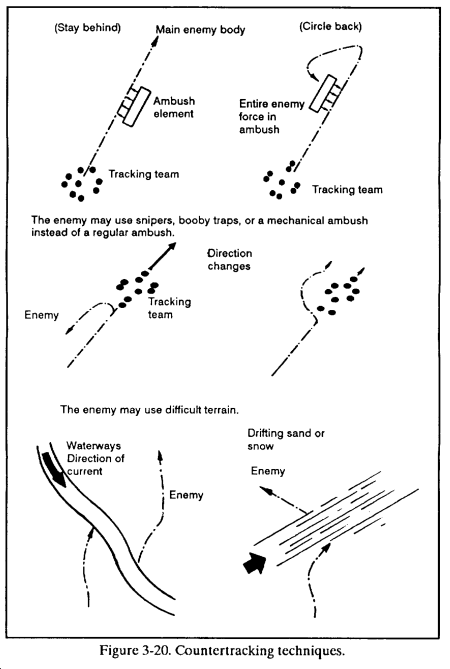
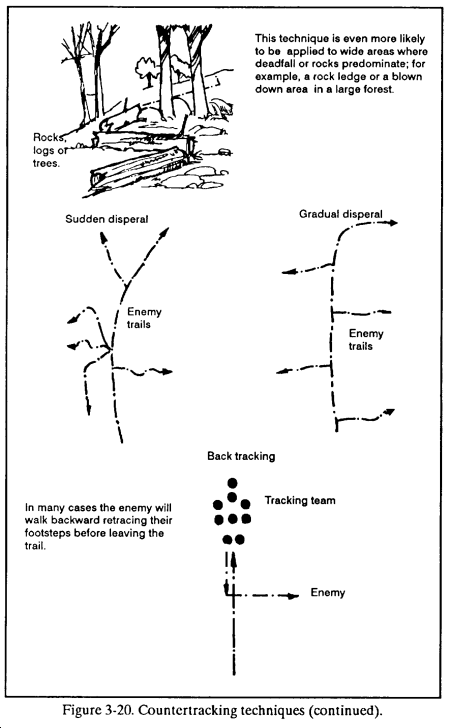
(2) Employing common countertracking techniques. Once the enemy realizes he is being followed, he will try to evade or attack the tracking team ( Figure 3-20 ).
c. Multiple Patrols. Two or more tracking teams can be used to track the same enemy unit.
EXAMPLE
1st Squad is tracking the enemy (Figure 3-21). The squad leader informs platoon headquarters (at the ORP) by radio and tells them the estimated size, composition, rate of march, and direction of travel of the enemy. The platoon leader directs 2d Squad on a route that will cut the enemy’s trail.
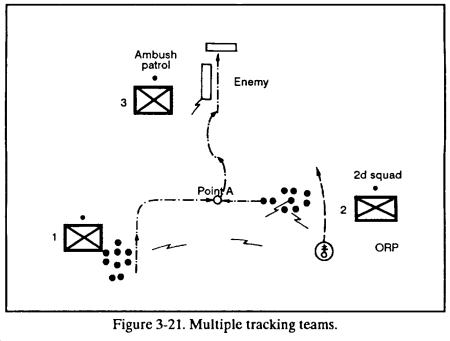
2d Squad marks where they cut the trail (Point A) and begins tracking. The mark is by prearranged signal. It can be a stake driven into the ground, several stacked rocks, or a twist of grass tied up and bent at an angle.
1st Squad continues to follow the trail until it reaches the mark left by 2d Squad. This ensures that the enemy unit is still together and that 2d Squad has found the correct trail. The leader of 1st Squad then requests further orders from the ORP.
When 2d Squad confirms the enemy unit’s direction, speed, and estimated distance, 2d Squad gives this information to the ORP. The platoon leader directs 3d Squad (which is patrolling in sector) to set up an ambush along the probable enemy avenue of approach.
Section V. PATROL BASES
A patrol base is a position set up when a squad or platoon conducting a patrol halts for an extended period. Patrol bases should be occupied no longer than 24 hours, except in an emergency. The platoon or squad never uses the same patrol base twice. Platoons and squads use patrol bases–
-
To stop all movement to avoid detection.
-
To hide during a long, detailed reconnaissance of an objective area.
-
To eat, clean weapons and equipment, and rest.
-
To plan and issue orders.
-
To reorganize after infiltrating an enemy area.
-
To have a base from which to conduct several consecutive or concurrent operations such as ambush, raid, reconnaissance, or security.
3-30. SITE SELECTION
The leader selects the tentative site from a map or by aerial reconnaissance. The site’s suitability must be confirmed; it must be secured before occupation. Plans to establish a patrol base must include selecting an alternate patrol base site. The alternate site is used if the first site is unsuitable or if the patrol must unexpectedly evacuate the first patrol base.
3-31. PLANNING CONSIDERATIONS
Leaders planning for a patrol base must consider the mission and passive and active security measures.
a. Mission. A patrol base must be located so it allows the unit to accomplish its mission.
b. Security Measures. Security measures involve the following.
(1) The leader selects–
-
Terrain that the enemy would probably consider of little tactical value.
-
Terrain that is off main lines of drift.
-
Difficult terrain that would impede foot movement such as an area of dense vegetation, preferably bushes and trees that spread close to the ground.
-
Terrain near a source of water.
-
Terrain that can be defended for a short period and that offers good cover and concealment.
(2) The leader plans for–
-
Observation posts.
-
Communication with observation posts.
-
Defense of the patrol base.
-
Withdrawal from the patrol base to include withdrawal routes and a rally point, or rendezvous point or alternate patrol base.
-
A security system to make sure that specific soldiers are awake at all times.
-
Enforcement of camouflage, noise, and light discipline.
-
The conduct of required activities with minimum movement and noise.
(3) The leader avoids–
-
Known or suspected enemy positions.
-
Built-up areas.
-
Ridges and hilltops, except as needed for maintaining communication.
-
Roads and trails.
-
Small valleys.
3-32. PATROL BASE OCCUPATION
A patrol base is established using the following steps. a. The patrol base is reconnoitered and established the same as an ORP or RRP, except that the platoon will enter at a 90-degree turn (Figure 3-22.)
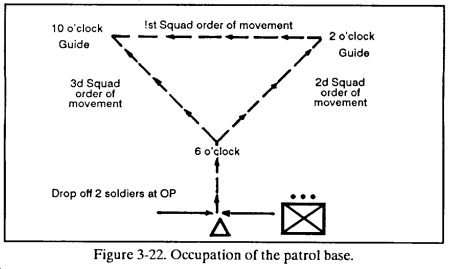
NOTE: This action is METT-T dependent; if there is nothing to be gained by doing this step, then the unit does not do it (for example, flat desert terrain.
b. The platoon leader leaves a two-man OP at the turn. The platoon sergeant and the last fire team will get rid of any tracks from the turn into the patrol base.
c. The platoon moves into the patrol base as depicted in Figure 3-22. (Squads will occupy a cigar-shaped perimeter.)
d. All squad leaders move to the left flank of their squad sector.
e. The platoon leader and support element or weapons squad leader start at 6 o’clock and move in a clockwise manner adjusting the perimeter (meeting each squad leader at his squad’s left flank). If the platoon leader and support element leader find a better location for one of the machine guns, they reposition it.
f. After the platoon leader has checked each squad’s sector, the squad leader and another squad member report to the CP as an R&S team.
g. The platoon leader issues the three R&S teams a contingency plan and remind them that they are looking for the enemy, water, built-up areas or human habitat, roads and trails, and any possible rally points. (Squads occupying patrol base on their own do not send out R&S teams at night.)
h. The R&S team departs from the left flank of their squad’s sector and moves out a given distance, as stated by the platoon leader in his instructions. The team moves in a clockwise direction and reenters the patrol base at the right flank of their squad’s sector. The R&S team, if at all possible, should prepare a sketch of the squad’s front and report to the CP.
NOTE 1: The distance the R&S team moves away from the squad’s sector will vary depending on
the terrain and vegetation (anywhere from 200 to 400 meters). All members of the
platoon are on 100 percent alert during this time. The R&S team is of little value at night
without the use of night vision devices. The RATELO must be able to establish
communications with higher headquarters using a directional antenna.
NOTE 2: If the platoon leader feels that the platoon may have been tracked, he may elect to
maintain 100 percent security and wait awhile in total silence before sending out the R&S
teams.
i. Once all squad leaders (R&S teams) have completed their reconnaissance, they report back to the platoon leader at the CP.
j. The platoon leader gathers the information from his three R&S teams and determines if the platoon is going to be able to use the location as a patrol base.
3-33. PATROL BASE ACTIVITIES
If the platoon leader determines that he will be able to use the location as a patrol base, he gives the following information to his platoon sergeant and squad leaders. Platoon leader also disseminates other information such as daily challenge and password, frequencies, call signs. Squad leaders return to their squads, give out information, and begin the priorities of work as stated by the platoon leader. The patrol base must be sterilized upon departure.
a. Security. Only one point of entry and exit is used. Noise and light discipline are maintained at all times. Everyone is challenged. Squad leaders supervise the placement of aiming stakes and ensure Claymores are put out. Each squad establishes an OP and may quietly dig hasty fighting positions. Squad leaders prepare and turn in sector sketches to include range cards.
b. Alert Plan. The platoon leader states the alert posture (for example, 50 percent or 33 percent) and the stand-to time for day and night. He sets up the plan to ensure positions are checked periodically, OPs are relieved periodically, and ensure that at least one leader is up at all times.
c. Withdrawal Plan. Platoon leader designates which signal to use if contact is made (for example, colored star cluster), the order of withdrawal if forced out (for example, squads not in contact will move first), and the rendezvous point for the platoon (if the platoon is not to link up at an alternate patrol base).
d. Maintenance Plan. Platoon leader ensures that machine guns, other weapon systems, communication equipment, NVDs are not broken down at the same time for maintenance. Redistribute ammunition.
NOTE: Weapons are not disassembled at night.
e. Sanitation and Personal Hygiene Plan. The platoon sergeant ensures the platoon slit trench is dug and marked at night with a chemical light inside the trench. Squad leaders designate squad urine areas. All soldiers accomplish the following daily: shave; brush teeth; wash face, hands, armpits, groin, and feet; and darken (polish) boots. Soldiers ensure that no trash is left behind.
f. Mess Plan. No more than half of the platoon eats at one time.
g. Water Resupply. Platoon sergeant organizes a watering party. They carry canteens in an empty rucksack.
NOTE: Squads have the same requirements with their squad patrol base as platoons.
The platoon should remain in single file. The platoon sergeant follows directly behind the guide so that he can count each soldier that passes through the passage point. He gives the count to the guide, tells him how long to wait at the passage point (or when to return), and confirms the running password. If the platoon makes contact after it is past the departure point, it fights through. Soldiers return to the departure point only if they become disorganized. They then reoccupy the initial rally point and the leader reports to higher headquarters.